KNEE ARTHRITIS
Arthritis can affect many different joints in your body, with knees being a common place for arthritis and arthritic pain.
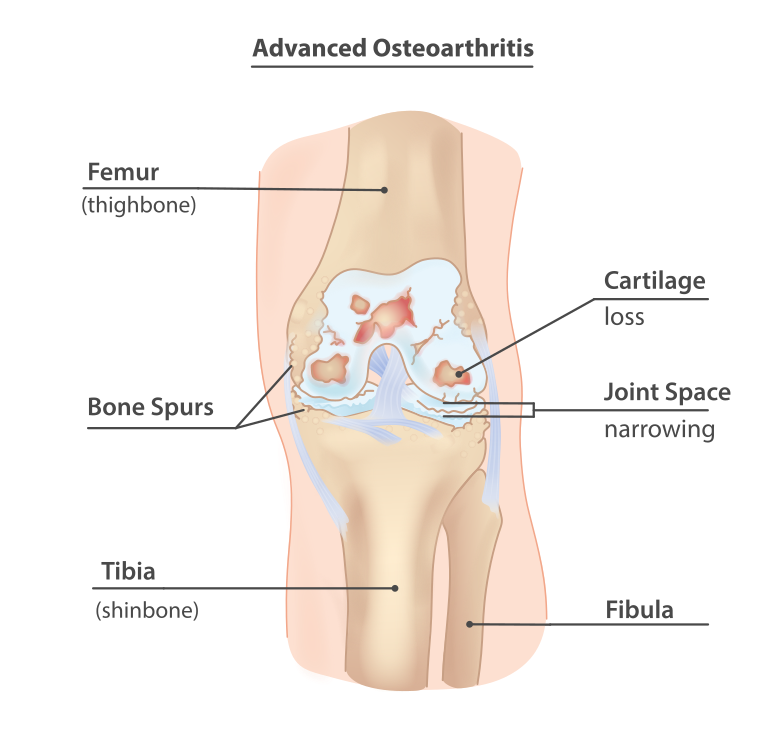
Arthritis is a degenerative disease that results in loss of cartilage, or cushion surrounding the ends of the bones. This condition is usually from overuse, or wear and tear over time. This kind of arthritis is called osteoarthritis.
Symptoms of Knee Arthritis
Pain: When the cartilage surrounding the bones in the knee joint breaks down, the bones become closer together. This loss of space (cartilage) can cause increased pain as the knee bones articulate with one another, particularly with weight-bearing activities or movement of the knee joint. Pain may be felt diffusely throughout the knee, or may be localized to a specific area depending on where the arthritis is located.
Decreased mobility: Pain is typically increased with weight-bearing activities such as rising from a chair, or walking. The motion of the knee joint may also be limited due to pain.
Knee Deformity: Depending on the location of the arthritis, you may develop a knee deformity or change in alignment of the knee. This may result in a bowing appearance (varus alignment) or a knock-kneed appearance (valgus alignment).
Additional symptoms include swelling, cracking or crepitus of the knee with movement, and stiffness of the knee joint, particularly in the morning.
Diagnosing Knee Arthritis
An X-ray is typically used to diagnose osteoarthritis of the knee. The X-ray will show a narrowing of the joint space between the femur (thigh bone) and tibia (shinbone). It may also show bone spurs and other signs of degeneration.
A physical examination from an orthopedic specialist or primary care provider can also aid in the diagnosis of arthritis. Examination may demonstrate a limited range of motion, swelling, and pain along the joint line.
Dr. Nelson can diagnose your knee arthritis and discuss solutions for your arthritis, whether that ranges from medication and lowered use of the knee to knee replacement surgery.
Treatment Options
Non-surgical
It is recommended that you initially treat knee pain caused by arthritis with non-operative interventions. Here are some of the non-operative treatment options:
- Activity modification
- Weight loss through diet and exercise
- Use of an assistive device (i.e cane, walker) to off-load the lower extremity
- Physical therapy to strengthen the surrounding knee musculature
- Medications such as Tylenol or NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatories)
- Knee injection (cortisone or visco-supplementation)
Dr. Nelson can offer some of these treatments himself or refer you to a physical therapist in your area who can help you lessen the pain in your knee. Preventing further deterioration is essential to minimizing current pain and future issues.
Surgical
If non-operative options are no longer beneficial, surgical intervention may be an option to treat knee pain caused by arthritis. Surgery is typically reserved for severe loss of cartilage and arthritis associated with progressive pain.
There are a couple of different options for surgery, including surgeries to repair a torn ligament or tendon, or full knee replacement if arthritis or injury has decreased the amount of cartilage in your knee too much to be comfortable.

Do I Need a Knee Replacement?
While a knee replacement is not our first recommendation, as many cases of arthritis can be treated without reconstructing a joint, knee replacement can be a great option for those who have extensive damage. Instead of trying to work with a joint that will permanently hurt, we can offer you the option of a new joint free of damage and pain.
A knee replacement joint has no arthritis and will fully integrate with the bones and tissue around it for an increase in stability and strength that you may have been missing before.
How Do I Know When to See a Doctor About Arthritis?
It’s important to see a doctor when arthritis starts to significantly affect your daily life. If you’re experiencing persistent joint pain, swelling, or stiffness that doesn’t improve with over-the-counter medications or home remedies, it’s time to seek medical attention. You should also visit a doctor if you notice a decrease in your ability to move or perform simple tasks, such as walking, climbing stairs, or gripping objects.
Early diagnosis and treatment can help manage symptoms and prevent further damage, so don’t wait if arthritis is impacting your quality of life.
What Causes Knee Arthritis?
Knee arthritis can develop from a variety of factors, and understanding these causes can help in preventing or managing the condition. Here are the primary causes of knee arthritis:
Wear and Tear (Osteoarthritis)
The most common form of knee arthritis, osteoarthritis, is caused by the gradual breakdown of cartilage in the joint due to aging and daily use. Over time, the cartilage that cushions the bones wears away, leading to pain, stiffness, and swelling as the bones rub against each other.
Injuries
Previous knee injuries, such as fractures, ligament tears, or meniscus damage, can increase the likelihood of developing arthritis later in life. These injuries can disrupt the normal structure of the knee joint, leading to cartilage deterioration over time.
Inflammation (Rheumatoid Arthritis):
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder that causes the immune system to attack the lining of the joints, leading to chronic inflammation. This inflammation can damage the cartilage and bone within the knee joint, causing pain and deformity.
Genetics
Some individuals may be genetically predisposed to developing arthritis, meaning they are more likely to experience joint issues due to inherited factors. If arthritis runs in your family, you may have a higher risk of developing knee arthritis, even if other risk factors are not present.
Obesity
Carrying excess body weight puts additional pressure on the knee joints, accelerating the wear and tear on the cartilage. Obesity is a significant risk factor for knee osteoarthritis because of the increased load on the joint with every step.
Overuse
Repetitive movements and overuse of the knee joint, particularly in certain occupations or sports, can lead to early-onset arthritis. Jobs or activities that require frequent kneeling, squatting, or heavy lifting can increase the stress on your knee joints.
Understanding these causes can help you take steps to protect your knee joints and prevent or slow the progression of arthritis. If you are experiencing knee pain or have a history of knee injuries, Dr. Nelson can help evaluate your condition and recommend the best treatment options for you.
Preventing Knee Arthritis and Slowing Its Progression
Taking proactive steps to protect your knees can help prevent knee arthritis or slow its progression if you’re already experiencing symptoms. Here are some tips to keep your joints healthy and maintain mobility:
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Carrying excess weight puts additional stress on your knee joints, increasing the risk of arthritis and worsening existing symptoms. By maintaining a healthy weight, you can reduce pressure on your knees and prevent further damage.
- Stay Active with Low-Impact Exercise: Regular exercise helps strengthen the muscles around your knees, providing better support and reducing joint strain. Focus on low-impact activities like swimming, cycling, or walking, which improve joint flexibility without causing further wear and tear.
- Protect Your Knees During Physical Activity: When engaging in sports or physical activities, use proper techniques and wear supportive footwear to reduce the risk of injury. Knee braces or pads can also offer added protection.
- Be Mindful of How You Use Your Knees: Be mindful of how you move, lift, and bend during daily activities. Using your legs to lift heavy objects and avoiding prolonged periods of standing or kneeling can help reduce stress on your knee joints.
You can always ask Dr. Nelson or your primary care doctor about taking supplements and adjusting your diet to include foods that will help your joints be healthy and strong for years to come.
By following these tips, you can protect your knees, reduce pain, and slow the progression of knee arthritis, helping you stay active and mobile.

Find Relief from Knee Arthritis
Don’t let knee arthritis hold you back any longer. Dr. Nelson offers a range of solutions, from non-surgical treatments to advanced knee replacement surgery, to help you manage pain and regain your mobility. Start by filling out our evaluation form, and our team will reach out to schedule your consultation at our Gilbert, AZ, office. Take the first step toward a pain-free, active lifestyle today.